Technical terms
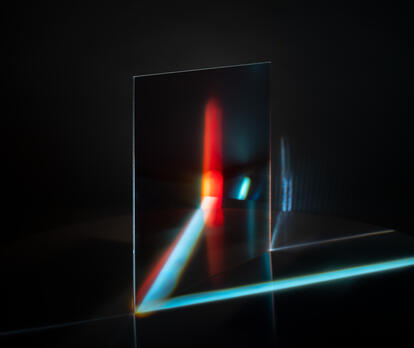
One of our core competencies and term that is looked up the most:
Dichroic glass / Dichroic filter
Interference-coated glass with light transmission for certain wavelength ranges (one specific colour) and reflection of the remaining ranges, i.e. they are not converted into heat through absorption.
The colour effect of dichroic filter layers varies with the wave angle and the viewing angle of the observer.
You can find out more about the technology and how it works here:
Dichroic glass in architecture, design and art:
Dichroic filters for lighting applications:
Further special terms:
Achromatic beam splitter
Colour-neutral, partially transparent mirror with reflection of a certain percentage of light and transmittance of the rest.
Anti-reflective coating
Interference system for reducing the reflection on glass surfaces. The residual reflection on any glass surface is typically less than 1 %.
Argon/Krypton
Inert gas for the enhancement of heat insulation for insulation glass.
Borofloat
Colour-neutral Borosilicate glass with high temperature and chemical stability produced using a floating process.
Chemical strengthening
Enhancement of the mechanical and thermal strength of the glass through special salt bath treatment.
We offer anti-reflective lenses that are chemically curable:
Entspiegelung
Interference system for minimising reflections (anti-reflection coating) of glass surfaces.
Development
Calculation of coating systems, sample production of coating solutions and systems in the laboratory with the goal of meeting new customer-specific requirements (order development).
ESG
Thermisch gehärtetes Glas, das durch einen Vorspannprozess eine stark erhöhte Schlag- und Biegefestigkeit erhält. ESG zerfällt bei einer Zerstörung in feine Krümel.
EVA
Ethylene-vinyl acetate plastic: Intermediate layer in laminated safety glass.
Farbeffektfilter / Farbeffektglas
Siehe Dichroitische Filter (oben)
FM types
Category of colour effect filters with low colour saturation.
FE types
Category of colour effect filters with medium colour saturation.
FS types
Category of colour effect filters with high colour saturation.
Float glass
High-quality, transparent flat glass manufactured using the so-called "floating process".
Half mirror
Colour-neutral, adsorption-free, partially transparent mirrors with reflection of a certain percentage of light and transmittance of the rest.
Interference
Interaction of two light beams, where - depending on the relation between them - amplification or annihilation occurs.
Interference principle, interference layer technology
Transparent thin layers with certain thickness and optical features are applied in a special sequence on a glass substrate. The reflected light fractions of the individual layers interfere with each other which leads to amplification or reduction of certain wavelength ranges - depending on the layer system design.
IR mirror
Dichroic mirror, which reflects the IR part of the light but lets the visible radiation pass.
IR radiation
Infrared radiation (thermal radiation): invisible radiation that heats up absorbing materials.
Isolierglas
Einheit aus mindestens zwei Glasscheiben. Der Abstand wird durch Abstandhalter gewährleistet.
Wärmedämmglas
Isolierglas mit verbesserten Wärmedämmeigenschaften durch die Verwendung von low-e-Schichten und Edelgasen.
Schalldämmglas
Isolierglas, bestehend aus zwei oder mehreren Glasscheiben mit sinnvoll aufeinander abgestimmten Dicken und Abständen, mit Luft oder Spezialgasgemischen gefüllt.
Kaltlichtspiegel
Dichroitischer Spiegel, der den sichtbaren Anteil der auftreffenden Strahlung reflektiert, für Wärmestrahlung hingegen durchlässig ist.
Kaltlichtspiegel
Konversionsfilter
Farbfilter, mit dem die Farbtemperatur des Lichts Richtung Blau (kälter) oder Rot (wärmer) verändert oder Farbkorrekturen vorgenommen werden können. Anwendung z.B. in der Warenbeleuchtung.
PVB
Polyvinyl butyral: Synthetic intermediate layer in laminated safety glass.
SentryGlas® Dupont
Synthetic intermediate layer in laminated safety glass.
Sonnensimulationsfilter
Optischer Filter, der zusammen mit einer geeigneten Lichtquelle das solare Spektrum so gut wie möglich abbildet. Anwendung: bei der elektrischen Charakterisierung von Photozellen und zur Materialprüfung.
Sol-gel dip coating
Method for producing thin layers on glass substrates. The glass is dipped into different solutions of organic metal compounds and drawn out at a defined speed. The film on the glass surface is transformed into adhesive metal oxide layers in the subsequent thermal process. By varying the materials, the number of layers and the layer thickness (depending on the drawing speed), it is possible to adjust the optical effects of the layer systems.
Stoßverbund, Stoßen
Gläser mit begrenzter Abmessung können durch ein spezielles Verbundverfahren auf einer Trägerglasscheibe zu einer größeren Abmessung verarbeitet werden. Daneben ermöglicht diese Technik auch die Darstellung von Mosaiken (Inlays) in unterschiedlichen Farben und Größen.
Stuctual Glazing
Static effective adhesion of glass on a metal frame construction.
Stufenisolierglas
Isolierglaseinheit, die einen Scheibenüberstand aufweist. Wird vornehmlich bei Schräg- und Überkopfverglasungen eingesetzt.
Tauchbeschichtung
Sol-Gel-Beschichtungsverfahren, bei dem das Substrat unter konstanten Bedingungen aus der Beschichtungslösung herausgezogen wird. Dabei bildet sich aus dem Sol durch Einfluss der Luftfeuchte ein Gel, welches durch einen Temperprozess in ein Metalloxid überführt wird.
Thermal tempering
Enhancement of the mechanical and thermal strength of the glass through thermal treatment (heating up, followed by fast, defined cooling down). We offer thermally curable antireflection coatings, e.g. for displays:
TVG
Teilvorgespanntes Glas: Vorgespanntes Flachglas mit erhöhter Schag- und Biegefestigkeit. Das Bruchbild ähnelt dem von Floatglas.
U-value
Heat transfer coefficient: Measuring unit for the heat lost through the glazing. Is specified in W/sqm K.
UV, VIS and NIR range
Characteristic wavelength for the crossover from the exclusion range (ultraviolet) to the transmission range (longer wavelength) of the filter where the transmission is 50%.
UV filter
It is differentiated between UV absorbing and UV reflecting filters.
UV filter edge
Characteristic wavelength for the crossover from the exclusion range (ultraviolet) to the transmission range (longer wavelength) of the filter where the transmission is 50%.
VG
Verbundglas besteht aus mindestens zwei Flachgläsern, die mit einer PVB-Zwischenlage miteinander verbunden sind.
Wärmereflexionsfilter
Dichroitischer Spiegel, der den IR-Anteil der auftreffenden Strahlung reflektiert, für die sichtbare Strahlung hingegen durchlässig ist.
Weißglas
Floatglas mit geringem Eisenoxyd-Anteil, um den "Grünstich" des Glases zu vermeiden.



